Verilog Sign Changer
Verilog Sign Changer
Purpose:
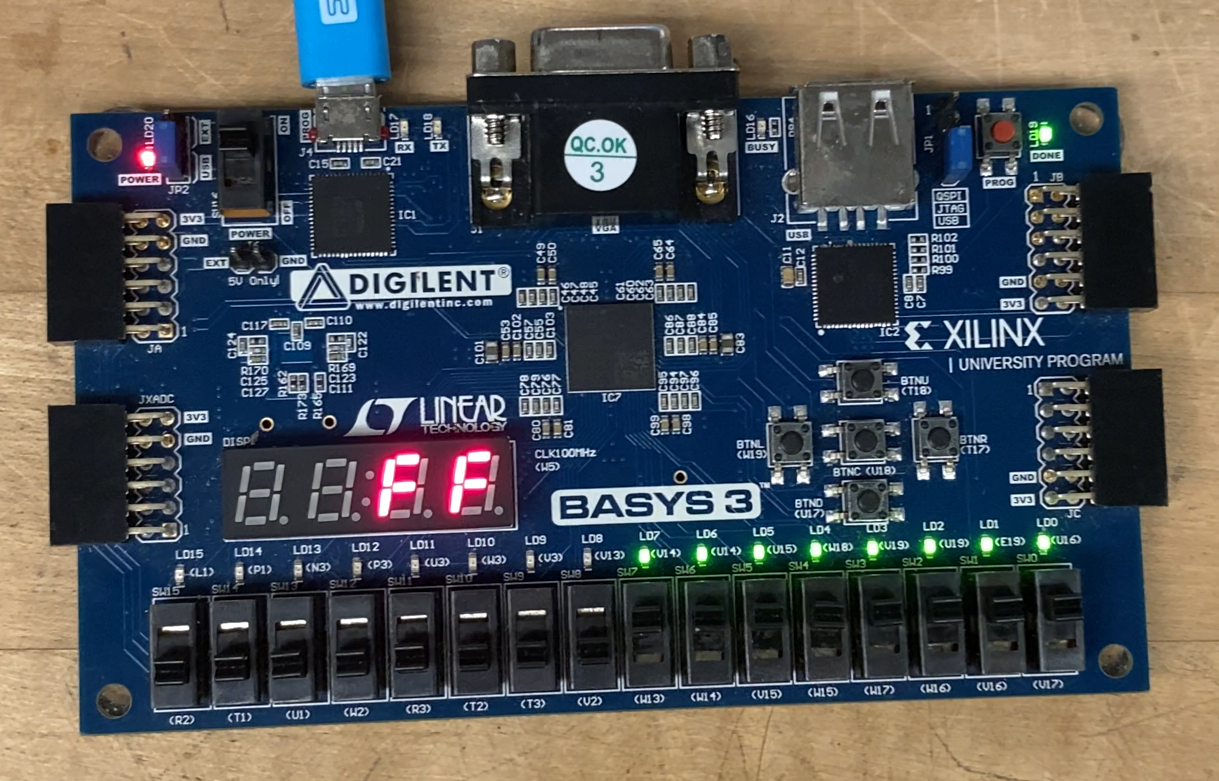
In this lab, you will design and implement several fundamental combinational logic components entirely in Verilog—specifically, an 8-bit adder (built from full adders), a 2-to-1 multiplexer for two 8-bit buses, a hex-to-7-segment encoder, and an 8-bit adder/subtractor—and then integrate them into a top-level module that performs a two’s-complement sign change on an 8-bit input. When the sign input is low, the output simply mirrors the input; when the sign input is high, the circuit outputs the two’s-complement negation of the input and detects overflow conditions (e.g., changing –128 to +128) by illuminating the decimal point on the display. Finally, you will instantiate two copies of the hex-to-7-segment converter and use a slow “digsel” signal, driven by a provided clock divider, to alternately drive the rightmost two digits of a Basys3 board’s seven-segment display—thereby presenting the 8-bit result in hexadecimal form and visually indicating any overflow.